Fusion Welding Challenges and Solutions
The use of advanced metallic alloys such as titanium has seen significant growth, particularly in sectors like aerospace, sports cars, nuclear, and process industries. These materials are prized for their high strength-to-weight ratio and exceptional corrosion resistance, making them indispensable in high-performance applications. In the aerospace industry alone, the titanium content in wide-bodied aircraft has increased by over 22% in the last five years.
While these alloys offer tremendous advantages, their fabrication—primarily through fusion welding—requires a specialised approach to avoid contamination and preserve mechanical strength. Fusion welding of these alloys, such as titanium, presents challenges that have been recognised for decades. Historical research, including a comprehensive NASA report from 1965, highlighted the critical importance of pre-weld cleaning and the use of protective gas during welding to prevent oxidation and contamination.
Contamination during welding can drastically reduce the flexibility of the weld metal and adjacent heat-affected zones, potentially leading to cracks even under moderate stress. To mitigate this risk, thorough cleaning of the weld area is essential. Oils, greases, and other contaminants must be meticulously removed, and protective gloves should be used during handling to prevent the introduction of foreign materials. Additionally, dedicated tools and workstations should be employed to minimise the risk of cross-contamination from other metals.
Another critical factor in welding high-performance alloys is protecting the weld and heat-affected zones from atmospheric exposure. Exposure to oxygen, even in small amounts, can lead to embrittlement and a reduction in mechanical properties. Therefore, shielding these areas from the atmosphere until they cool below 400°C is crucial. While vacuum welding processes such as electron beam welding offer excellent protection, they are often prohibitively expensive and impractical for anything other than large-scale production of identical components.
A more practical solution for many applications is using inert gas shielding during welding. The effectiveness of this shielding can often be gauged by the colour of the weld, which indicates the extent of oxidation. For example, a bright, silvery weld is generally considered a sign of good shielding, whereas darker colours indicate varying degrees of exposure to oxygen and, consequently, reduced weld quality.

Argweld® Weld Trailing Shields®
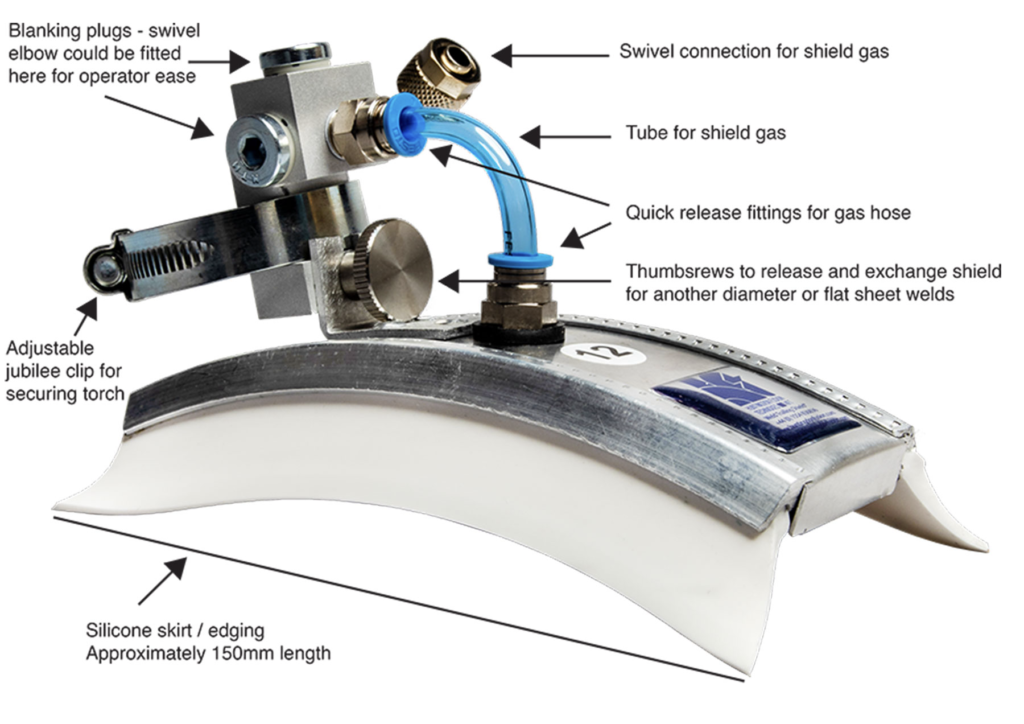
Huntingdon Fusion Techniques Ltd developed the Argweld® Weld Trailing Shield® over 50 years ago to provide optimal protection during fusion welding. These shields have since become an industry standard, providing critical inert gas coverage to the solidified weld metal and the adjacent heat-affected zones until they cool below 400°C. The Argweld® Weld Trailing Shield® has undergone numerous redesigns to incorporate the latest technological advancements, ensuring it remains at the forefront of welding protection technology.
The Argweld® Weld Trailing Shield® is specifically designed for GTAW (TIG) and PAW (plasma) welding torches, providing a high level of supplemental inert gas shielding beyond what the basic torch can offer. These shields come in models suited for both flat sheet welding and radiused versions for external and internal welding of pipes or circumferential tank welding. They are available in various configurations to accommodate different welding processes, material thicknesses, and specific welding needs.
Key features of the Argweld® Weld Trailing Shield® include a multi-mesh gas distribution system that ensures even, non-turbulent gas flow over the weld surface. The shield is equipped with quick-connect ports for feeding inert gas behind the fusion zone, and a unique clip design allows different shield sizes to be used without changing the welding torch. The shield's silicone skirts also provide a reliable seal between the shield and the workpiece, while a fine mesh filter above the fusion zone minimises turbulence within the cavity.
The extensive range of Argweld® Weld Trailing Shields® can accommodate various welding scenarios, including non-linear profiles with curvatures as small as 25 mm in diameter. This versatility makes them suitable for a wide range of applications, from aerospace to motorsports, where the integrity of the weld is paramount.
Choosing the Right Argweld® Weld Trailing Shield®
Selecting the appropriate Argweld® Weld Trailing Shield® involves considering several factors, including the extent of oxidation that needs to be controlled, the thickness of the material being welded, the welding process being used (as PAW has a different heat input than GTAW), and the required welding speed and current.
References
Further Information
Huntingdon Fusion Techniques Ltd is a technology-led company with an extensive library available to its customers on request. This library includes many internal technical documents, many of which have been published internationally. For more details, visit Weld Trailing Shields or Instagram.
Published Papers